 Where to Start?
Where to Start?
First, expand the usual scope of wellness activity to well-BEING. Include initiatives that support more than just physical fitness, such as career growth, social needs, financial health, and community involvement. By doing this you increase your chances of seeing a return on investment (ROI) and a return on value (ROV). Qualitative results of a successful program are just as valuable as seeing a financial impact of a healthier population.

Source: Katherine Baicker, David Cutler, and Zirui Song, “Workplace Wellness Programs Can Generate Savings,” Health Affairs, February 2010, 29(2): pp 304-311
To create a corporate culture of well-being and ensure the success of your program, there are a few important steps.
- Leadership Support: Programs with leadership support have the highest level of participation. Gain leadership support by having them participate in the programs, give recognition to involved employees, support employee communication, allow use of on-site space, approve of employees spending time on coordinating and facilitating initiatives, and define the budget. Even though you do not need a budget to be successful.
- Create a Committee or Designate a Champion: Do not take this on by yourself. Create a well-being committee, or identify a champion, to share the responsibility and necessary actions of coordinating a program.
- Strategic Plan: Create a three-year strategic plan with a mission statement, budget, realistic goals, and measurement tools. Creating a plan like this takes some work and coordination, but the benefits are significant. You can create a successful well-being program with little to no budget, but you need to know what your realistic goals are and have a plan to make them a reality.
- Tools and Resources: Gather and take advantage of available resources. Tools and resources from your broker and/or carrier can help make managing a program much easier. Additionally, an employee survey will help you focus your efforts and accommodate your employees’ immediate needs.
How to Remain Compliant?
As always, remaining compliant can be an unplanned burden on employers. Whether you have a wellness or well-being program, each has their own compliance considerations and requirements to be aware of. However, don’t let that stop your organization from taking action.
There are two types of programs – Group Health Plans (GHP) and Non-Group Health Plans (Non-GHP). The wellness regulations vary depending on the type of employer and whether the program is considered a GHP or Non-GHP.
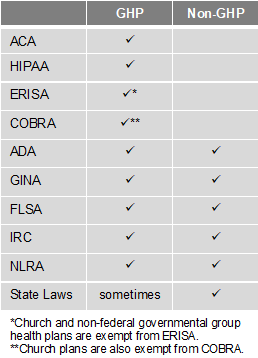
Employers looking to avoid some of the compliance burden should design their well-being program to be a Non-GHP. Generally, a well-being program is Non-GHP if it is offered to all employees regardless of their enrollment in the employer’s health plan and does not provide or pay for “medical care.” For example, employees receive $100 for attending a class on nutrition. Here are some other tips to keep your well-being program Non-GHP:
- Financial: Do not pay for medical services (e.g., flu shots, biometric screenings, etc.) or provide medical care. Financial incentives or rewards must be taxed. Do not provide premium discounts or surcharges.
- Voluntary Participation: Include all employees, but do not mandate participation. Make activities easily accessible to those with disabilities or provide a reasonable alternative. Make the program participatory (i.e., educational, seminars, newsletters) rather than health-contingent (i.e., require participants to get BMI below 30 or keep cholesterol below 200). Do not penalize individuals for not participating.
- Health Information: Do not collect genetic data, including family medical history. Any medical records, or information obtained, must be kept confidential. Avoid Health Risk Assessments (i.e. health surveys) that provide advice and analysis with personalized coaching or ask questions about genetics/family medical history.
Hope DeRocha
Originally Posted By www.ubabenefits.com
